Introduction Mobiluncus Mulieris
In this article, we will discuss Mobiluncus mulieris, a bacteria primarily known for causing infections in women. Our discussion will cover:
- Mobiluncus spp
- Mobiluncus bacterial infections
- Mobiluncus bacteria
- Mobiluncus curtisii treatment
First Half of the Main Content
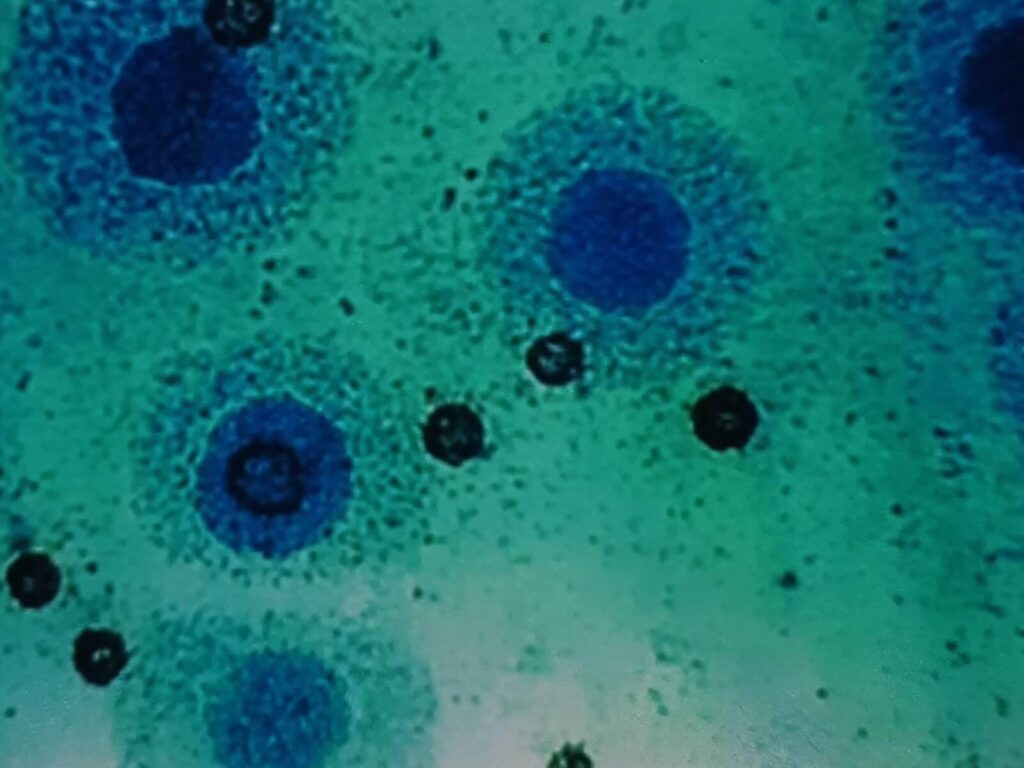
Mobiluncus spp is a group of bacteria predominantly composed of Mobiluncus mulieris and Mobiluncus curtisii.
These species have a unique curved shape and grow in various environments within the human body.
They are anaerobic bacteria, meaning they can thrive without the presence of oxygen.
Mobiluncus bacterial infection is most commonly seen in women suffering from bacterial vaginosis.
This prevalent condition affects millions of women worldwide and occurs when the natural balance of bacteria in the vaginal area is disrupted.
This imbalance leads to a change in the vaginal environment, allowing the growth of Mobiluncus bacteria, among other harmful microbes.
The presence of Mobiluncus bacteria can lead to various symptoms, including:
- Vaginal discharge with a strong, unpleasant odor
- Itching or irritation
- Pain during urination or intercourse
However, some cases produce no symptoms and are only detected during routine gynecological exams.
Second Half of the Main Content Early detection and treatment are essential to prevent complications such as:
- Pelvic inflammatory disease
- Preterm birth in pregnant women
- Higher risk of sexually transmitted infections
For this reason, it is vital for women experiencing unusual symptoms to seek medical advice promptly.
Mobiluncus curtis ii treatment typically involves the use of antibiotics prescribed by a healthcare professional.
A commonly prescribed antibiotic for this infection is Metronidazole, which may be administered orally or through a topical gel.
It is crucial to adhere to the recommended dosage and duration to ensure effective treatment.
It is also important to note that completing the antibiotic course is crucial, even if symptoms improve early on.
Failure to complete the treatment may lead to a recurrence of the infection or antibiotic resistance.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding Mobiluncus mulieris and its relation to bacterial vaginosis is critical for effective prevention and treatment.
With proper medical intervention and adherence to prescribed medications, women can minimize the risks and complications associated with Mobiluncus bacterial infections.
